Given values of two nodes in a Binary Search Tree, find the Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA). You may assume that both the values exist in the tree.
The function prototype should be as follows:
struct node *lca(node* root, int n1, int n2) n1 and n2 are two given values in the tree with given root.
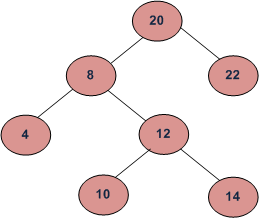
For example, consider the BST in diagram, LCA of 10 and 14 is 12 and LCA of 8 and 14 is 8.
Naive Thinking: Binary Search Tree 的题目一定要用上 左 < 中 < 右 这个性质。可以发现如果当前点是同时大于n1, n2 的,他们的LCA一定在当前节点的左子树,反之则在右子树。如果当前点在二者之间呢,说明这就是他们的LCA!
这是recursive的做法。
class TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x){
val = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
public TreeNode LCAinBinarySearchTree(TreeNode root, int n1, int n2){
return traversal(root, n1, n2);
}
private TreeNode traversal(TreeNode root, int n1, int n2){
if(root==null) return root;
if(root.val >= n1 && root.val <= n2) return root;
if(root.val > n1 && root.val > n2) return traversal(root.left,n1,n2);
else return traversal(root.right,n1,n2);
}
这是iterative的做法,用queue也可以,应该直接使用root作指针。这里好傻。
public TreeNode LCAinBinarySearchTree(TreeNode root, int n1, int n2){
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
if(root==null) return root;
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if(node.val >= n1 && node.val <= n2) return node;
if(node.val > n1 && node.val > n2 && node.left!=null) stack.push(node.left);
else if(node.right!=null) stack.push(node.right);
}
return null;
}
这是正确的做法。
public TreeNode LCAinBinarySearchTree(TreeNode root, int n1, int n2){
if(root==null) return root;
while(root!=null){
if(root.val >= n1 && root.val <= n2) return root;
if(root.val > n1 && root.val > n2) root = root.left;
else root = root.right;
}
return null;
}
Improved Way: 如果这两个值有可能不在BST里呢?应当在找到LCA的时候继续遍历下去找到两个值。
public TreeNode LCAinBinarySearchTree(TreeNode root, int n1, int n2){
if(root==null) return root;
while(root!=null){
if(root.val >= n1 && root.val <= n2 && findNode(root,n1) && findNode(root, n2)) return root;
if(root.val > n1 && root.val > n2) root = root.left;
else root = root.right;
}
return root;
}
// improved version: make sure existence of n1 and n2
private boolean findNode(TreeNode root, int n){
while(root!=null){
if(root.val == n) return true;
if(root.val > n) root = root.left;
else root = root.right;
}
return false;
}
No comments:
Post a Comment